The problem with plastic
Since 2012, Parley’s focus has been on plastic — here’s why
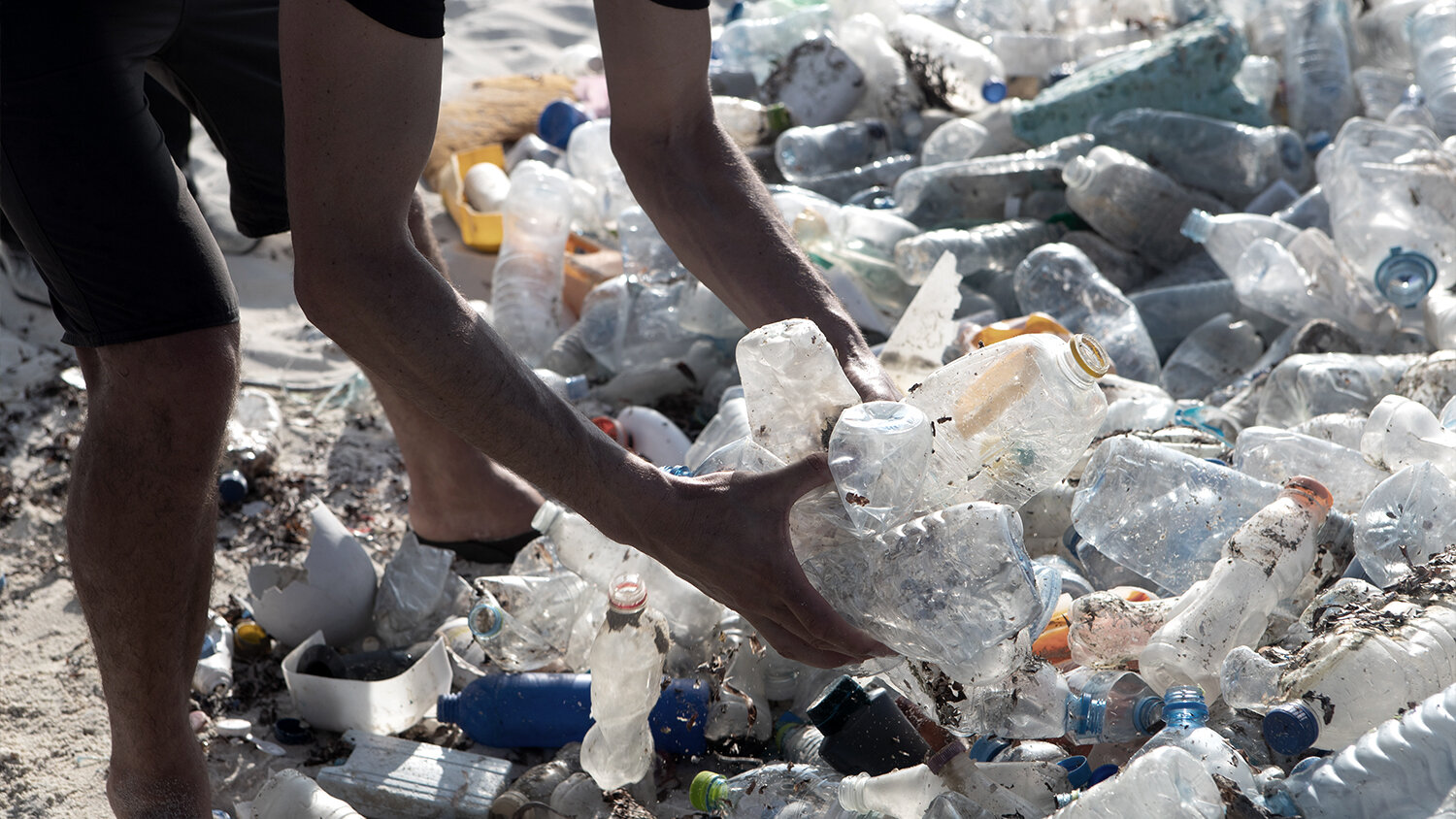
Photo by Giacomo Cosua
"Our strategy to end plastic pollution is to recognize the problem and accept that plastic is a design failure"
Cyrill Gutsch — CEO & Founder, Parley for the Oceans
Of all the serious issues currently threatening life in the oceans, plastic pollution is among the most pervasive, visible and relentless. You’ve probably heard all the familiar stats by now – 11 million tons of it enters the oceans every year, a garbage truck every minute, more plastic than fish by 2050 – but take a second to pause and really imagine the plastic reality we inhabit. Billions of plastic items are created and used briefly every day.
Less than 10% of all plastic is recycled, so the majority persists on our planet. Much of it ends up in airless landfills, destined to linger for hundreds or even thousands of years – but a massive amount escapes our waste systems, permeates the soil, flows continually down into our waterways and ends up in the oceans.
Once a piece of plastic touches the surface of a stream, river, lake or ocean it becomes very hard to recover. Over time, plastic accumulates in coastal ecosystems, coats the seafloor, strangles and starves marine life and, most insidiously, breaks apart into smaller and smaller fragments, becoming virtually impossible to ever clean up. These microplastics, and the others released by manufacturing, vehicle tires and textiles, have now been found from the peaks of the Pyrenees to the Arctic sea ice to the bottom of the deepest point of the Pacific Ocean.
Plastic is literally everywhere – it is in the air we breathe, the food we eat and the water we drink. Scientists have even found it inside our bodies. Most mind-blowing of all? Fossil fuel extraction and plastic production is set to increase drastically in the coming decades.
Why Plastic?
Plastic pollution isn’t the only threat to the survival of our oceans. Overfishing has stripped the oceans of 90% of big fish, putting entire ecosystems at risk. According to the UN, almost 33% of reef-forming corals and more than a third of all marine mammals are threatened. Climate change is rendering the very ocean water that supports life more warm and acidic, which could doom coral, phytoplankton and other fundamental ocean species. Agricultural runoff is creating vast dead zones in places like the Gulf of Mexico, and dumping at sea (both routine and illegal) kills off marine life with toxic substances that can persist and accumulate in species like killer whales.
These issues are vital, and Parley supports efforts within our Network and beyond to address them. But as we’ll see, plastic is inextricably linked to carbon emissions, fishing, industrial pollution and other issues. If we can solve these massive problems working together, nature is powerful and resilient. If we tackle emissions soon, the oceans can cool. Pesticides and other toxins will disperse. Fish stocks can recover, often within a decade. But plastic will persist for thousands of years, and plastic is our problem. We drive its unnecessary creation, and we – the creative community – must own the issue. The fashion industry, e-commerce, food delivery services, product packaging and all the other plastic-wrapped commodities that underpin our lifestyles need to be redesigned. We can create novel new materials and systems that co-exist with nature instead of destroying it. We are the people who need to tackle this.
In 1973, the first PET plastic single-use bottle was introduced. Today, 1 million of them are consumed globally every single minute – packaging our most essential resource in a material that never biodegrades. Although recyclable, the vast majority of plastic bottles used globally end up in landfills, in rivers, in our oceans and washed up on the world’s coastlines. In the presence of oxygen and UV rays from the sun, the polymer chains that give plastic its strength begin to fail, creating brittle and discolored plastic that easily shatters and breaks apart. This process actually releases CO2 into the atmosphere, and creates microplastic pieces that are almost impossible to intercept – permeating beaches, dunes, riverbanks and the wider ecosystem.
What is Plastic?
Let’s briefly go back to basics and explore exactly what plastic is. Before 1907, modern synthetic plastic didn’t even exist on Earth. Since then, we have created an ever-expanding number of new plastics. The word itself comes from the Greek “plastikos” – meaning moldable. Dating back 3500 years, bio-based plastic was naturally derived from the sap of gum trees to make rubber-like artefacts. Later examples of polymer materials include silk, wool, glass and rubber.
Today, the term “plastic” is used to describe synthetic materials belonging to the polymer family. Polymers are made up of chains of repeating carbon-containing, shorter compounds called monomers. Plastic monomers are built on hydrogen and carbon atoms (hydrocarbons), which are extracted from fossil fuels. Chemists are able to make different types of plastic qualities based on the monomer composition and arrangement.
The process of producing plastic begins with the extraction of crude oil. It contains ethylene and propylene – the two hydrocarbons that make up monomers. Through a process known as cracking, the hydrocarbons are broken down into smaller molecules and turned into hydrocarbon monomers. Polymerization then takes place, which links the the molecules together to form polymers called resins. During this process, ethylene is converted into the resin polyethylene and propylene into polypropylene. Crucially, this can include the addition of plasticizers, dyes and flame-retardant chemicals. The resins are cooled down and cut to form pellets or beads, sometimes called nurdles, which are transported to manufacturers to make products.
Photo by Emily Penn — eXXpedition
Pellets & Microplastics
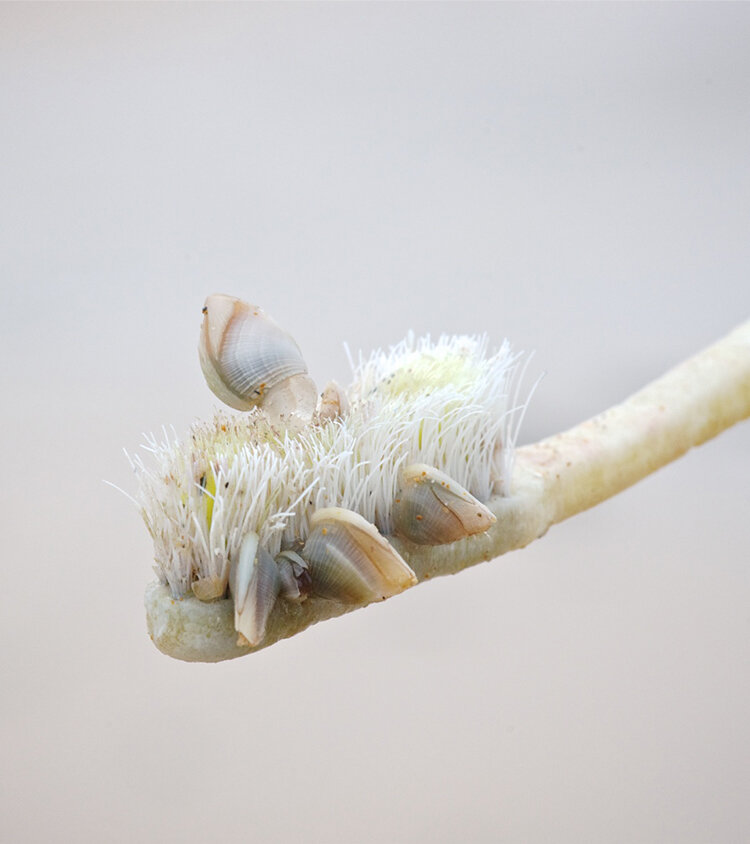
Long before it becomes the all-too-familiar marine pollution you find at the beach, plastic enters the environment in other forms. Pellets and nurdles can and do spill out at every stage of their journey – from refinery to finished products. Researchers in the Gulf of Mexico have uncovered extensive and devastating nurdle pollution, and a massive pellet spill on a Hong Kong beach in 2012 showed the inherent risks of shipping them around the world.
Once they hit the water, nurdles and microplastics can absorb bacteria and chemical contaminants from surrounding environments. In marine wildlife studies, microplastics have been shown to transfer these harmful chemicals from their plastic hosts onto—or into—tissues, which in turn adversely affects the animals. At a nanometer in size, plastic fibers can penetrate cells, which means they can make their way into organs.
It’s not just marine life at risk. A 2018 study tested 259 bottled waters from 11 leading brands worldwide. Six sampled bottles were glass, the rest were packaged in plastic. All the bottles had plastic bottle caps. Plastic debris contamination was widespread throughout, with 93% of sampled bottles containing microplastic particles and a global average of 325 particles per liter of bottled water. One bottle showed an excess of 10,000 microplastic particles per liter — enough to make you never want to drink from a plastic bottle again.
Photo from ALBATROSS by Chris Jordan
Ingestion and Entanglement
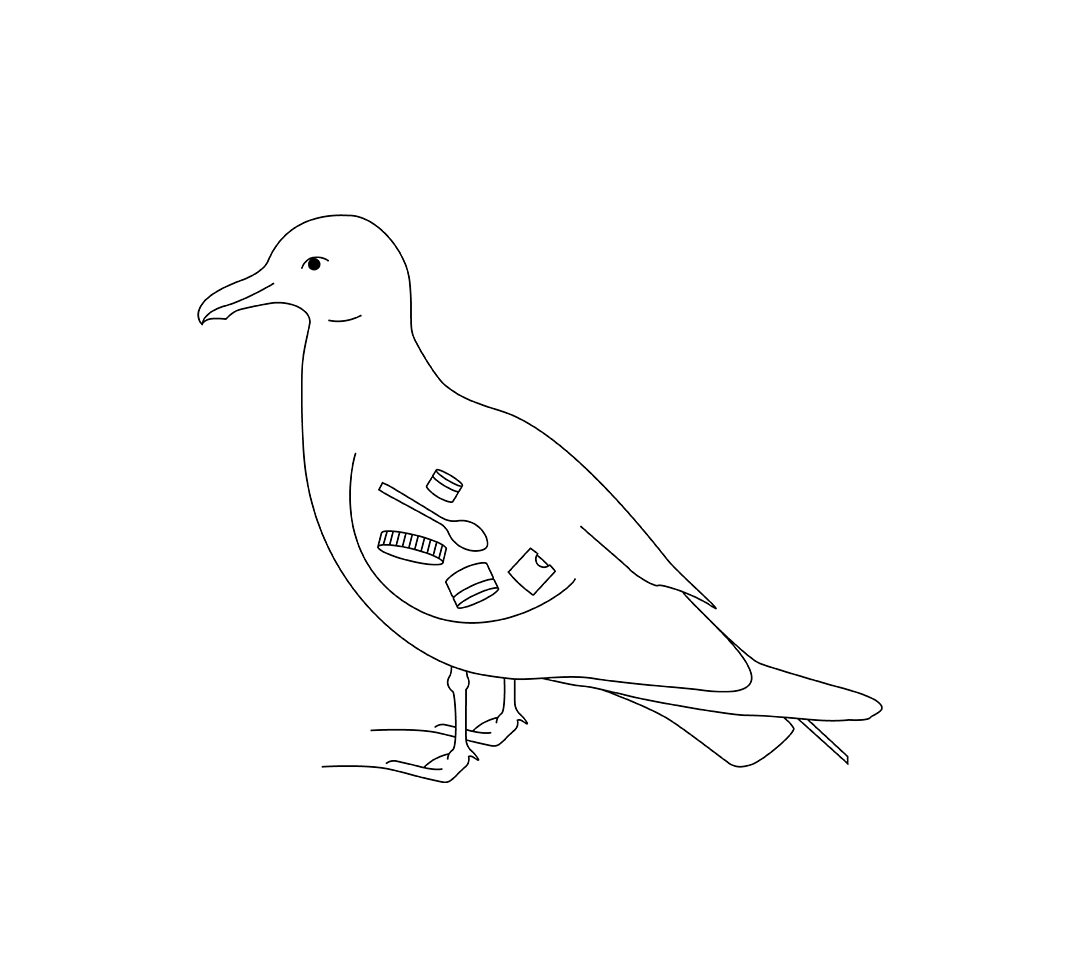
The very durability and flexibility that makes plastic so useful also makes in pretty immortal. In the ocean environment, plastic slowly breaks apart – but not before taking a heavy toll on wildlife. More than 100,000 marine mammals die every year from entanglement in plastic debris. Whales wash ashore with stomachs full of plastic bags, cups, bottles and other everyday detritus. Almost all of the world’s seabirds and sea turtles have ingested plastic.
If we fail to replace plastic and halt the continued pollution of the oceans, we are facing the potential extinction of many sea life species and the interruption of the entire marine ecosystem. We also risk the survival of our own species – since over 4.3 billion depend on the oceans for food, many in small island developing states.
Photo by Lisa Wollett
Photo by Lisa Wollett
Plastic Chemicals
Beyond the damage caused by the material itself, many plastics come with extra baggage in the form of toxic chemicals used to make it softer, or harder, or more fire-resistant, or other properties. In the ocean environment, these chemicals can concentrate in the fish and marine mammals that consume plastic.
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and phthalate compounds have been found in whales and dolphins, where they can affect growth and reproduction patterns. The same blubber that insulates animals like killer whales from the frigid oceans can also become a storehouse for such chemicals, leading to depleted populations like those off the US and Canadian west coast.
A few years back, plastic pollution pioneer and Parley ambassador Emily Penn tested her blood specifically for chemicals banned by the United Nations. Out of 35 banned chemicals, Emily’s blood contained 29. These included traces of pesticides and flame retardants, which are especially concerning in terms of women’s health. Endocrine disruptors mimic hormones that can impact women’s pregnancies and be passed onto offspring through childbirth and breastfeeding.
Photo by Caroline Power Photography
Plastic & Climate Change
The production of plastic is intrinsically linked to climate change. Already, 6% of global oil consumption goes towards creating plastics – and for certain types of plastic like polyethylene (PET) the rate of carbon emissions can be as high as 6:1. So for every kilogram of plastic produced, 6 kilograms of CO2 is emitted into the atmosphere. The average plastic drink bottle for instance, comes with .4 of a kilogram of carbon emissions.
In 2018, Parley Science Advisor and marine plastics researcher Dr. Sarah-Jeanne Royer and her colleagues at the University of Hawaii revealed another, previously unknown link between plastics and climate change. They demonstrated that many plastics actually give off powerful greenhouse gases as they break down, contributing to climate change. Of particular concern is the plastic type which releases gases at the highest rate: low-density polyethylene (or LDPE). This is also the most prevalent discarded plastic in the ocean today.
LDPE has a weaker and less dense chemical structure than most plastics, meaning it breaks down more easily. The more surface area a piece of plastic has, the more gas is given off. A plastic bottle, for example, after years of photo-degradation, will have a surface area thousands of times greater than its original surface area. Over time, plastics give off more and more gas. Light (and to a lesser extent heat) are the primary catalysts for this gaseous release. This leads to an alarming feedback loop: as the climate changes, the planet gets hotter, the plastic gives off more methane, increasing the rate of climate change and the circle continues.
Plastic Facts & Stats
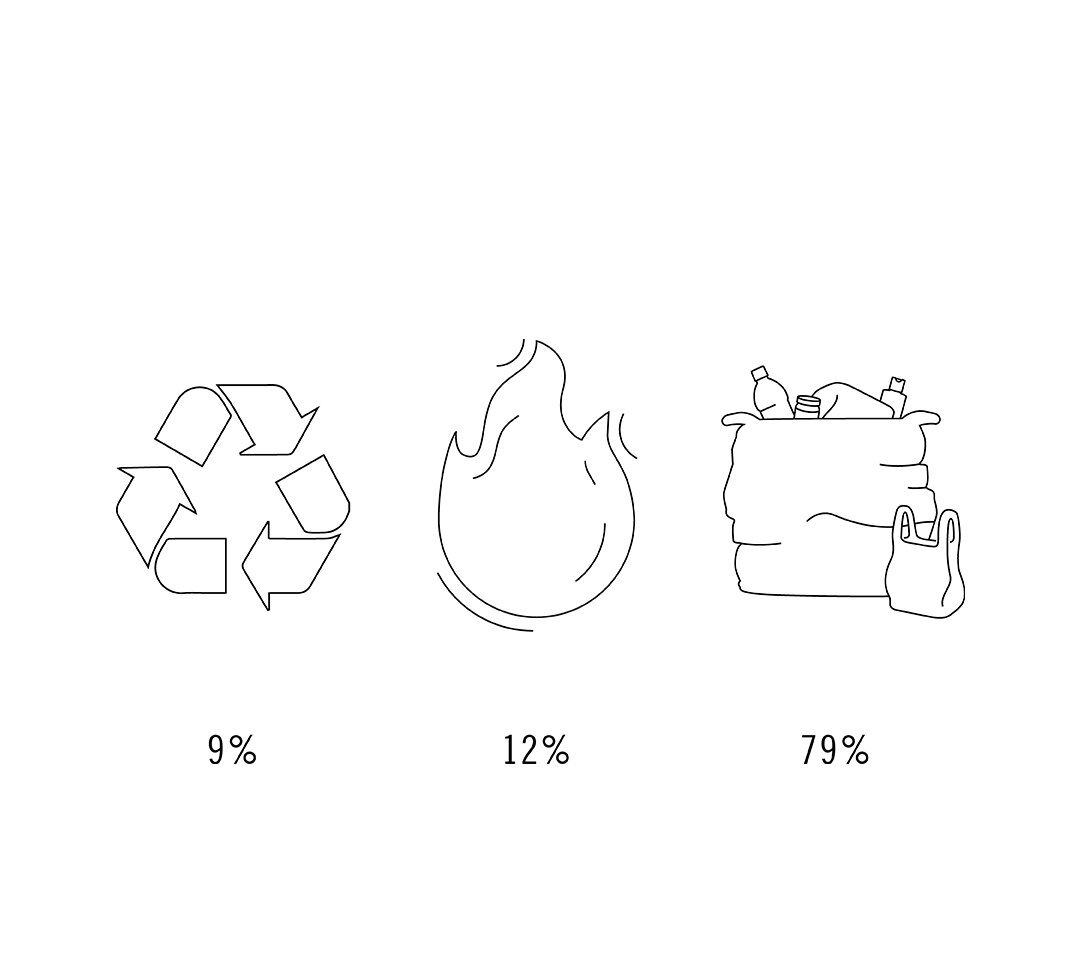
Just 9% of plastic has been recycled, 12% incinerated and 79% has accumulated in landfills or the wider environment.
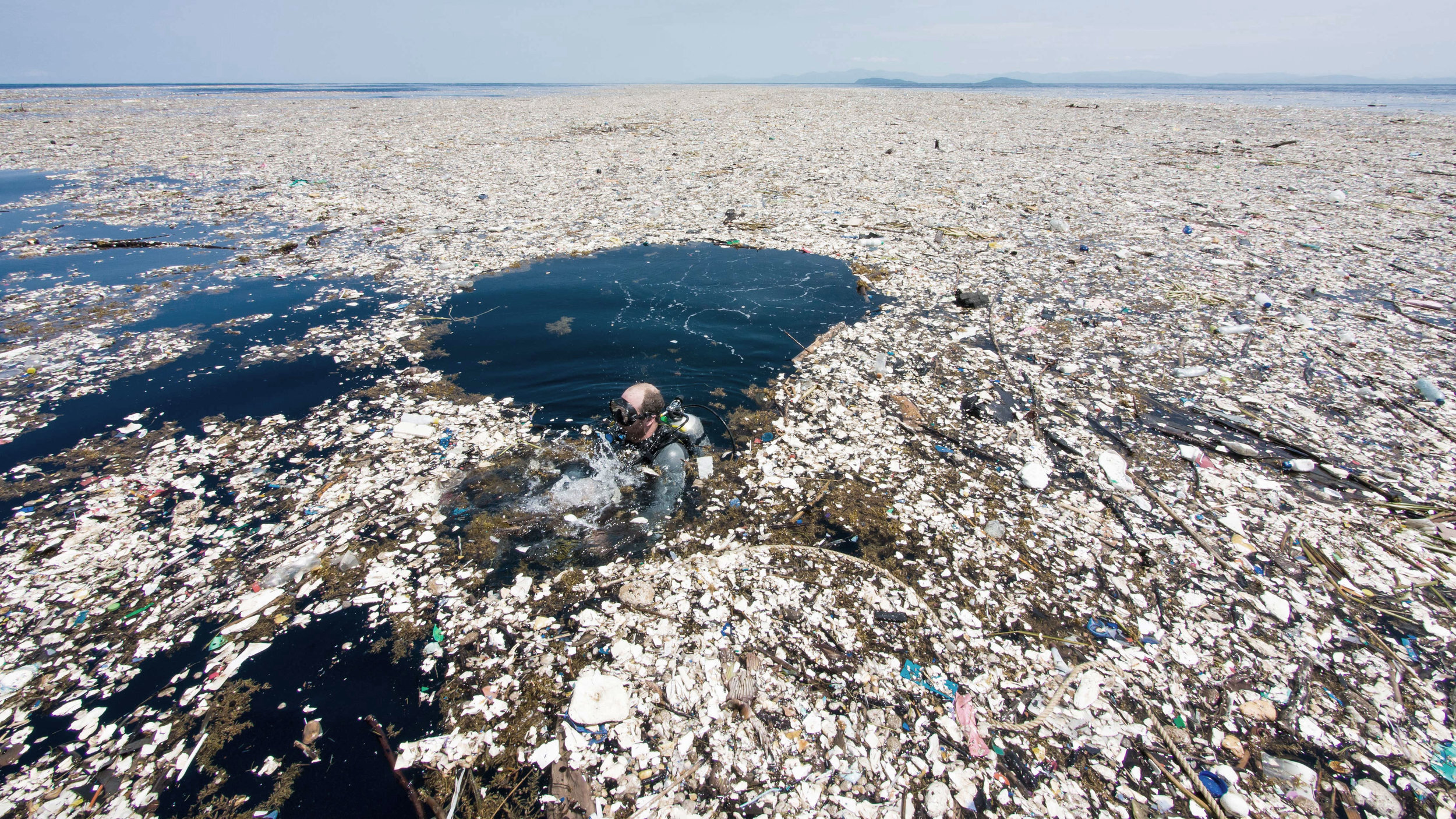
At least 5.25 trillion pieces of plastic are currently floating in the world’s oceans. About 11 million tons of plastic enters the ocean each year.
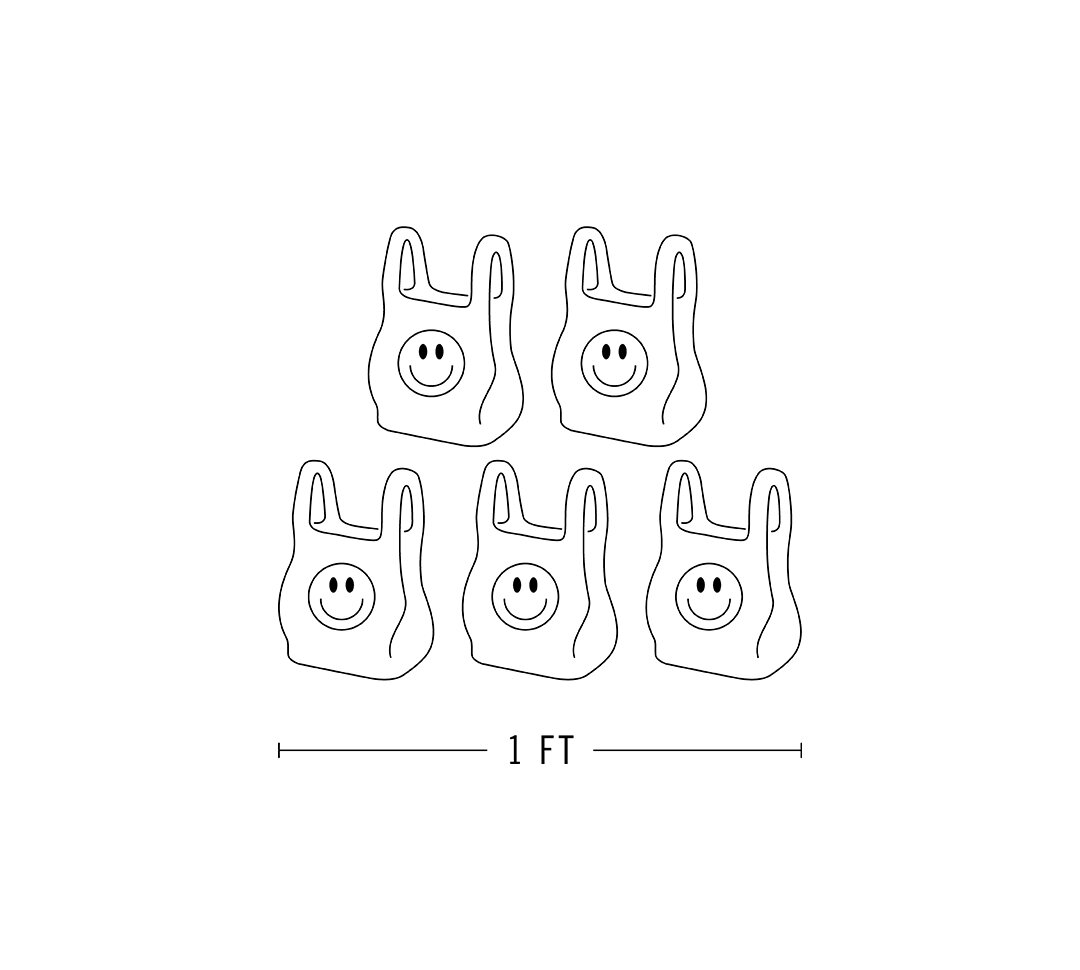
Enough plastic enters the oceans each year to fill 5 grocery bags per foot of coastline. By 2025, this number could increase to 10 grocery bags.
The rate of plastic use is exploding. Nearly half of all plastic ever manufactured has been made since 2000.
Over 1 trillion plastic bags are used every year worldwide, or 2 million each minute.
40 percent of plastic produced is packaging, used just once and then discarded. Only 14 percent of packaging is properly recycled.
By 2050, there could be more plastic in our oceans than fish.
90% of seabirds have ingested plastic. Nearly all seabirds will have plastics in their stomachs by 2050.
If plastics usage continues as expected, the plastics sector will account for 20% of total oil consumption and 15% of the global annual carbon budget by 2050.
Human ingenuity and imagination created synthetic plastics before we considered their impact. Creativity and innovation can help us end this nightmare.
Parley AIR Strategy
AVOID PLASTIC | INTERCEPT PLASTIC WASTE | REDESIGN THE MATERIAL ITSELF
#ParleyAIR